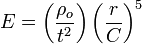- 5,141
- 290
Normally we use this calculator to find out the power of an explosion (http://www.stardestroyer.net/Empire/Science/Nuke.html)
But the minimum power insertable is 0,001 MT, which gives a "air-blast radius" minimum of 280 meters, so my question is: how to find the power of an explosion of a radius smaller than 280 meters? (In this case, I have a blast radius of 163.65 meters)
But the minimum power insertable is 0,001 MT, which gives a "air-blast radius" minimum of 280 meters, so my question is: how to find the power of an explosion of a radius smaller than 280 meters? (In this case, I have a blast radius of 163.65 meters)